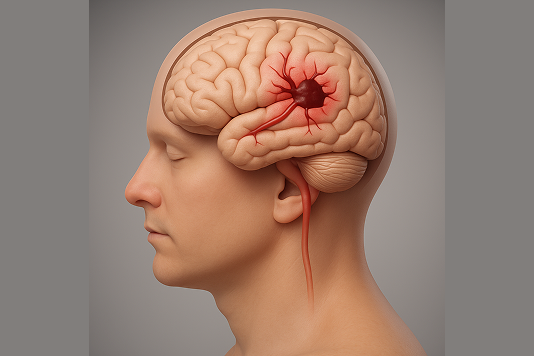
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die within minutes.
There are two main types :
| Letter | What It Means | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| F | Face Drooping | Ask the person to smile. Does one side droop? |
| A | Arm Weakness | Ask them to raise both arms. Does one drift down? |
| S | Speech Difficulty | Ask them to repeat a sentence. Is it slurred or strange? |
| T | Time to Call Doctor/Hospital | If any sign is present, call emergency services immediately. |

A migraine is more than just a headache — it’s a neurological condition that can cause intense, throbbing head pain, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sound.
Migraines can occur in 4 stages (not everyone experiences all) :
Acute (for attacks) :
Preventive :
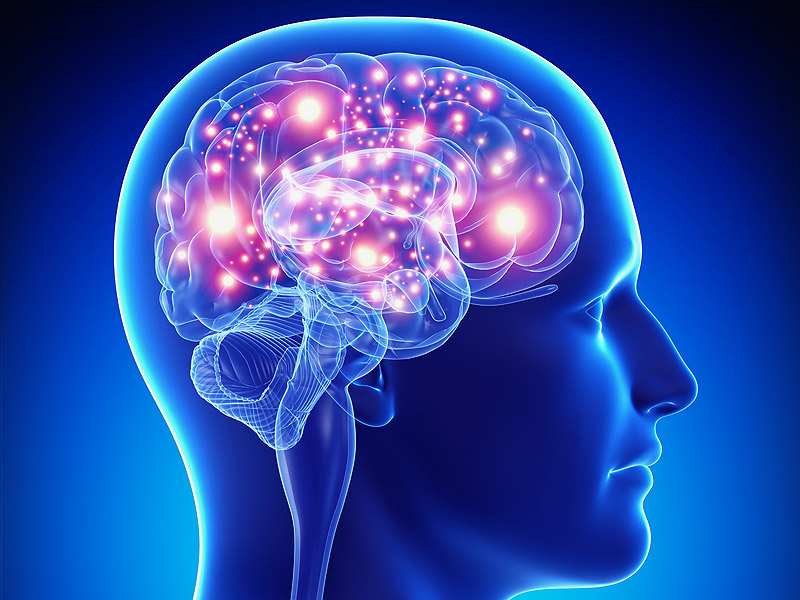
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures. It can affect anyone, at any age.
Seizures vary widely. The two main categories are :
1. Focal Seizures (Partial)
2. Generalized Seizures
May include :
If someone is having a seizure :
In many cases, the cause is unknown. But possible causes include :
While epilepsy is a lifelong condition for many, it can often be managed with :
About 70% of people with epilepsy can control seizures with medication.
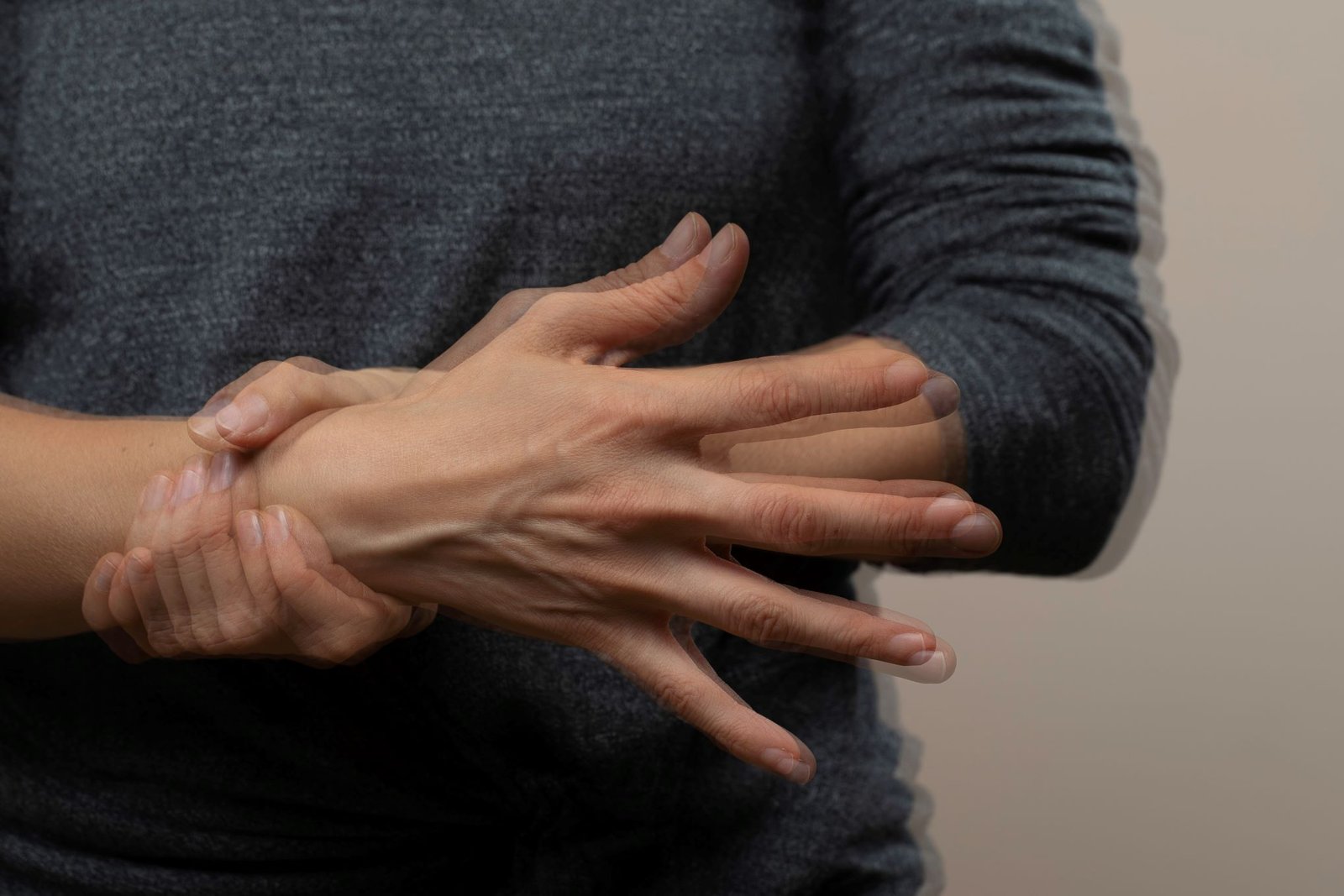
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurological disorder that affects movement. It happens when brain cells that produce dopamine — a chemical that helps control movement — begin to die.
Parkinson’s symptoms develop slowly and vary from person to person. Common symptoms include :
Parkinson’s progresses in stages, from mild symptoms (stage 1) to severe disability (stage 5). However, progression varies widely.
Risk Factors :
There is no cure, but treatments help manage symptoms
Medication :
Therapies :
Advanced Options :